Introduction
we delve into Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and FEA services, it is necessary to understand what Finite Elemental Method (FEM) means. FEM is a precursor to understanding FEA.
The basic concept behind Finite Elemental Method is to replace any complex shape with the summation of a large number of regular / simple shapes (like a rectangle, triangle, etc.).
These shapes are then combined to correctly model the original part. These smaller, simpler shapes are called finite elements because each such shape occupies a finite sub-space within the original, complex shape. For example, it is easier to visualize an engine, airplane, a machine component or skeleton as made up of smaller, simpler components. It makes modelling easier. And unlike finite difference models, finite elements do not overlap in space.
Figure 1: FEA Simulation of a piston rod. The different colors are indicators of variable values that help predict mechanical behavior.
What is Finite Element Analysis (FEA)?
FEA is thus a numerical method that offers a means to find approximate solutions to complex mechanical engineering problems. FEA methods contrast to the infinitesimally small or differential elements used for centuries to derive differential equations.
FEA has traditionally been a branch of Solid Mechanics. However, with the advent of sophisticated CAD and CAE tools, FEA is now used to solve design problems in mechanical and other engineering fields like aerospace and defence, automotive, electrochemical and consumer goods.
Here are the steps involved in FEA:
1. Divide the interval of integration - the numerical result is an approximation to exact solution.
2. In each sub-interval, choose proper simple functions to emulate the true function - the accuracy of numerical result depends on the number of sub-interval and approximate function.
Areas of FEA Application
A FEA is the most common tool for stress and structural analysis. It can also receive input data from other tools like kinematics analysis systems and computation fluid dynamics systems.
Example application of FEA – Axle. Observe mesh on critical parts being refined to capture sensitive quantities like stresses and strains.
FEA software can be used in:
- Mechanical Engineering design
- Advantages of FEA in mechanical engineering design are :-
- can be used to demonstrate a new design concept that would help the engineering team predict its possible real-world behavior under diverse load environments. Based on this analysis, any suitable alteration can be easily made before finalizing the drawing.
Fig. 3
- The biggest strength of Finite Element Analysis techniques is the sensitive software used to deliver in-depth and precise analysis of various physical and functional aspects of materials, systems, products, 3D CAD designs etc.
Structures are made up of infinite number of atoms. Any structure built requires to be tested for its structural integrity.
For example If engineers were to analyze a simple structure theortically, for stress analysis, they would have to calculate the stress value on each atom( practically impossible!)to prove its safe design.

Fig. 4
Hence we use Finite Element Method to help us evaluate the stress values. In finite element method, infinite atoms are replaced by finite nodes and the bonds are replaced by elements. This makes sense from engineering point of view as it is now practically possible to evaluate stress values at finite locations than at infinite points.
The goal of modal analysis in structural mechanics is to determine the natural mode shapes and frequencies of an object or structure during free vibration. It is common to use the finite element method (FEM) to perform this analysis because, like other calculations using the FEM, the object being analyzed can have arbitrary shape and the results of the calculations are acceptable. The types of equations which arise from modal analysis are those seen in eignsystem.
Fig. 5
The physical interpretation of the eigenvalues and eginvectors which come from solving the system are that they represent the frequencies and corresponding mode shapes. Sometimes, the only desired modes are the lowest frequencies because they can be the most prominent modes at which the object will vibrate, dominating all the higher frequency modes.
The finite element method (FEM) is a computer technique for solving partial differential equations. One application is to predict the deformation and stress fields within solid bodies subjected to external forces. However, FEM can also be used to solve problems involving fluid flow, heat transfer, electromagnetic fields, diffusion, and many other phenomena.
The principle objective of the displacement based finite element method is to compute the displacement field within a solid subjected to external forces.
Mold flow computes the injection molding process where plastic flows into a mold and analyzes the given mold design to check how the parts react to injection and ensure that the mold will be able to produce the strongest and uniform pieces.
- Fatigue & Fracture Mechanics
Fatigue failure occurs when a material is subjected to repeated loading and unloading cycles. The level of stresses present to cause failure may be well below values considered safe for a single static load application. The critical fatigue initiation is usually at a very localized site and may be a result of additional factors such as stress concentration due to component shape, surface finish or corrosion pitting.
Fig.7
Fatigue has been cited as one of the major causes of in-service failure throughout engineering history. The nature and prediction of fatigue is now much more understood, and is a requirement for most design products today. However the application of fatigue analysis is not easy and a good background is essential to be able to use the powerful FEA method as a basis for fatigue analysis.
- Thermal and Electrical analysis
A method is developed to predict the effective thermal conductivity and thermal resistance of the woven fabric by using finite element method (FEM). Repeating unit cell of the fabric is developed by using the actual parametric value of the fabric by using scanning electron microscope (SEM) and then analyse these unit cell by applying different boundary conditions.
The predicted effective thermal conductivity and thermal resistance value of fabric are compared with experimental value.
- Sheet Metal forming analysis
Fig.8
Today the metal forming industry is making increasing use of simulation to evaluate the performing of dies, processes and blanks prior to building try-out tooling. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is the most common method of simulating sheet metal forming operations to determine whether a proposed design will produce parts free of defects such as fracture or wrinkling.
Finite Element Modeling and Simulation of Car Crash
Safety is one of the design considerations in automobile community. Therefore, crash test is an important step to validate the novel car design. However, high cost in experimental testing limits the number of crash tests, and adequate data might not be obtained consequently. Alternatively, numerical modeling and simulation have been widely used to study car crash in addition to experimental testing. As a powerful numerical tool, finite element method (FEM) plays an vital role in crash test simulations.
we simulated a car crashing into the wall virtually to understand the devastating outcome that car crashes can have on automobiles. To simplify the study, only the car frame was considered in our studies. The car model was generated in the 3d modeling software CREO and then imported to the FEM analysis software ANSYS for mesh generation and FEM analysis. We adopted quasi-static simulation tool in ANSYS, and employed the conservation of linear momentum to calculate the time-averaged force acting on the car during the impact. Therefore, the wall was not modeled in our studies. Various incoming velocities were considered, and the car deformation was compared to the one from a real life testing.
The design of the car frame was generated in the 3D modeling software CREO, where the car was created as a life size model to accurately examine the effects of a car crash.
The dimensions of the car were researched online on the Ford website and translated into the design in CREO.
As mentioned before, only the frame of the explorer was generated in order to analyze how the frame structure deforms during the impact of a crash.
Isometric view of the Ford Explorer in real life :-
Isometric view of the Ford Explorer inCREO :-
The geometry was exported as an IGS file from CREO and then imported into ANSYS for mesh generation and FEM analysis. Upon importing the geometry, the material was set to aluminum alloy for the car body. The mass of a Ford Explorer is approximately 2458kg, based on the information on the Ford website.
Mesh generation for the Ford Explorer in ANSYS :-
A fine mesh was placed on the front of the car to accurately depict the event of a crash, where a wall would hit the whole front of the car rather than at different points on the fender, which is what a coarse mesh would provide.
Then the nodal forces, applied at the nodes as shown in Figure
Applied nodal forces on contact points of car :-
Various incoming speeds, from 20mph to 100mph in increments of 20mph, were considered here as the speeds of car before impact.
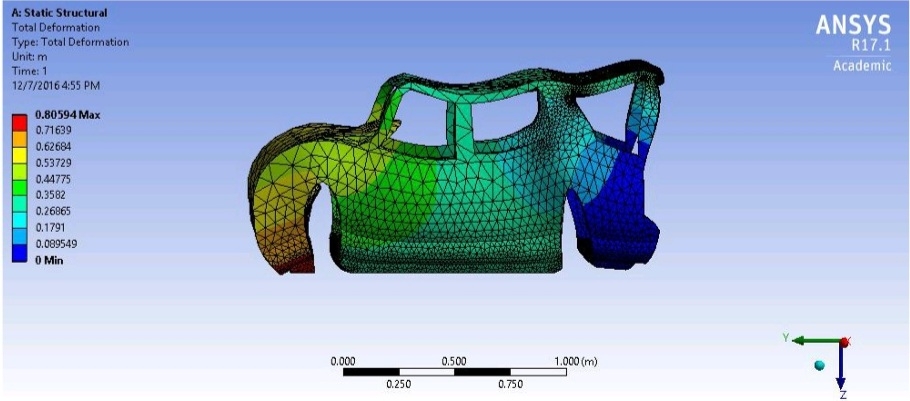
The deformed configurations of car after impact are shown in Figures below
A) Total deformation of car at 20mph
B) Total deformation of car at 60mph
C) Total deformation of car at 100mph
Conclusion :-
The numerical modeling and simulation of car crash have been carried on in automobile companies for years. Finite element analysis can generate realistic results that help scientists and engineers understand the way that cars are effected by different crash scenarios. Instead of running real life situations, it is much more cost effective to simulate car crash using a commercial software such as ANSYS.
References :-
Mahendran, Mahen (2007) Applications of Finite Element Analysis in Structural Engineering.
Clough, Ray W. and Joseph Penzien, Dynamics of Structures, 2nd Ed., McGraw-Hill Publishing Company, New York, 1993, page 173
Bathe, Klaus Jürgen, Finite Element Procedures, 2nd Ed., Prentice-Hall Inc., New Jersey, 1996, page 786
https://www.brown.edu/Departments/Engineering/Courses/En1750/Notes/FEA_Intro/FEA_Intro.htm
http://www.autoform.com/en/products/solution-tryout-part-production/application-examples-tryout-part-production/
T. Belytschko, W.K. Liu and B. Moran, Nonlinear Finite Elements for Continua and Structures, 1st ed. U.S.: Wiley, New York, 2001.
Lin C. S., Chou K. D. and Yu C. C., Numerical simulation of vehicle crashes, Appl. Mech. Mat. 590, 135 (2014).
Kankariya N. and Sayyad F. B., Numerical simulation of bumper impact analysis and to improve design for crash worthiness, Int. J. Engrg. Sci. 4(5), 58 (2015).
Sun T., Liu T., Shen I F. and Ma Y. S., Numerical simulation of car rash analysis based on distributed computational environment, Conference Proceeding, 5th Int. Conference on Algorithms and Architectures for Parallel Processing, Pp 334-337, (2002).














Insightful..
ReplyDelete